- The Bitcoin trilemma helps explain why the blockchain has very low transaction speeds
- Improvements in scalability can boost functionality and promote BTC adoption
The most recent Bitcoin [BTC] halving occurred on 19 April 2024. The blockchain’s mining reward was slashed to 3.125 BTC, reducing supply and forcing miners to optimize their hardware. It also reinforced the scarcity of Bitcoin, making it a viable alternative as a store of value.
Michael Saylor, co-founder and former CEO of MicroStrategy [MSTR], realized how he could use this mechanism to his company’s advantage during the previous cycle. In fact, he sees it as a hedge against inflation.
To secure his treasury against inflation, he is not afraid to use leverage to buy more Bitcoin. “The only use of time is to buy more Bitcoin. Take all the money and buy more Bitcoin. Then take all your time to figure out what you can sell to buy more Bitcoin,” he said in January 2024. The king of cryptos is up by nearly 115% since then.
His legendary conviction supports the idea that more and more institutions would add BTC to their treasuries.
Beyond being an investment and inflation hedge, what do users expect from the blockchain? What developments progressed in 2024, and what does 2025 likely have in store for BTC’s on-chain users?
Bitcoin trilemma
The three key aspects of a blockchain are scalability, decentralization, and security. Scalability refers to the ability to process transactions, decentralization is the distribution of decision-making and control across the blockchain, and security is the network’s ability to defend against fraud and attacks.
One of Bitcoin’s major challenges is scalability. Its Proof of Work mechanism and the ever-growing hash rate mean that Bitcoin is highly secure as a network. Decentralization is also not one of the major drawbacks, although, over the years, Bitcoin mining has become more centralized due to the emergence and growth of mining pools.
Source: CoinLedger
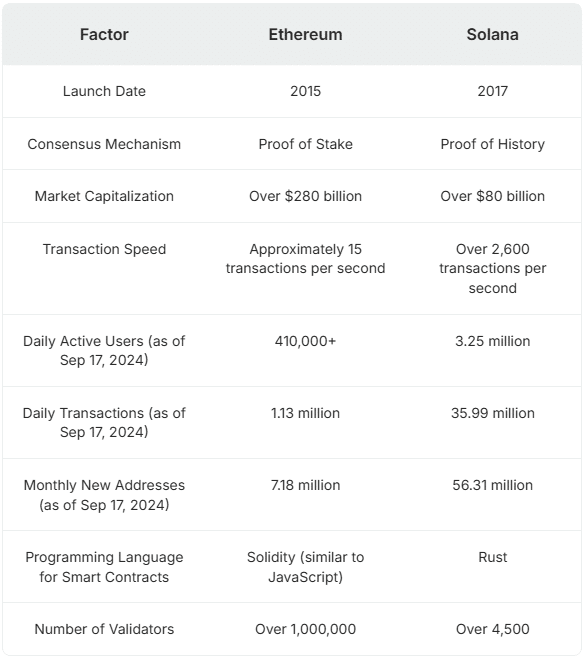
The Bitcoin blockchain can handle about 7 transactions per second (TPS) while Ethereum [ETH] and Solana [SOL] stand at 15 and 2,600 TPS, respectively. This is the blockchain trilemma. The concept highlights the trade-offs between security, decentralization, and scalability.
In order to have a high throughput, networks have to sacrifice security or decentralization and opt to have fewer nodes to enable a higher TPS. Meanwhile, highly decentralized networks struggle with efficiency and speed.
Solutions to the scalability problem
Over time, the popularity and number of users on the Bitcoin network are likely to increase. This would lead to greater user demand, and could also spark a necessity for the blockchain to enhance its utility and value to a user.
As a Layer 1, Bitcoin is built to have a low TPS and a limited number of use cases compared to chains like Ethereum or Solana which boast a robust decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. To achieve scalability and support more complex applications, the network has to look towards Layer 2 solutions.
Layer 2 solutions are built on top of an existing blockchains and do not need a network-wide consensus to deploy, unlike Layer 1 solutions. This makes them a more flexible and attractive solution option.
Some of the existing Layer 2s are Lightning Network, Stacks, and Merlin Chain. Stacks aims to bring smart contracts to Bitcoin without altering the original protocol. Initially called Blockstack, it was rebranded in October 2020. Stacks is a Bitcoin Layer for smart contracts, extending the network’s utility to include smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs (non-fungible tokens), and dApp (decentralized application) functionalities.
Lightning Network and its potential in 2025
Lightning Network was proposed in 2015 and has been operational since 2018. It aims to increase transaction speeds and reduce costs by allowing transactions to occur off the main blockchain.
And yet, it faces some challenges. The Lightning Network allows users to transfer by creating channels between them that can remain open for further payments. It slashes the transaction fee, bringing it to the region of $0.001 from the current $2.8 cost per transaction, and allows its completion in seconds.
LN had around 15,000 and nearly 54,000 payment channels as of August 2024, with a channel liquidity of just over 5,000 Bitcoin. It has seen the implementation of various new wallets such as Muun and Phoenix that improve the user experience. Growing adoption across Asia, Africa, and Latin America makes e-commerce more viable. LN usage is boosted by entities such as Bitrefill, a cryptocurrency gift card retailer, and OpenNode, a payment processor that enables merchants to accept BTC as payment.
In 2025, Lightning Network’s expansion to use stablecoins for payment apart from BTC would help achieve mass adoption. This integration with stablecoins can bring about real-world payments using crypto stablecoins and can allow foreign exchange transactions to be settled almost instantly anywhere across the globe.
Beyond Layer 2s
The future of Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions is full of potential, but there is a further evolution possible. Layer 3 solutions built on top of Layer 2 scalability aim to enhance interoperability and application-specific functionality.
Layer 3 can enable customizable functionality by tailoring for specific needs, and optimizing performance and efficiency. They can seamlessly connect different blockchains and different Layer 2 solutions, thereby expanding the possibilities of blockchain technology.
One example of a Bitcoin Layer 3 is Impervious, the browser built on top of Bitcoin. It is decentralized, and all data transmitted is done so privately, leaving no space for data surveillance. It is also censorship-free.
It uses the Lightning Network to process transactions, which means that messaging and sharing documents will be done almost instantly and later submitted to the blockchain. This would levy a fee for each transaction, but privacy could be worth it.
Another example of a Layer 3 solution outside of Bitcoin is Cosmos. It was designed to address the cacophony of blockchains by integrating them into an “internet of blockchains”. It offers secure data transfer between independent blockchains, and sharding is used for scalability. This enhances the potential for dApps by enabling the use of assets and functionalities from different blockchains.
Read Bitcoin’s [BTC] Price Prediction 2024-25
Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions can reshape the usage of the blockchain. By boosting lower transaction fees and faster speeds, it fosters adoption by the public even for micropayments and casual spending. Advancements along this path would mean that Bitcoin is not just a store of value, but would also be a practical medium for exchange – As it was originally envisioned.

